


Specially developed vitamin D3
for people over 65 years of age

The first vitamin D3 in Poland
based on the unique EmulOil® technology

Dosing consistent with the Recommendations:
2000 IU to 4000 IU
RECOMMENDATIONS

Experts alarm that 9 out of 10 people in Poland suffer from vitamin D3 deficiency.
The most frequent age-related reasons of vitamin D3 deficiency include:
- Intestinal malabsorption,
- Insufficient vitamin D3 synthesis in the skin which has not enough substances necessary to produce vitamin D3,
- Compromised function of the liver and kidneys where vitamin D3 is converted into its active form.
Therefore, the Recommendations on vitamin D3 supplementation in people over 65 years of age highlight the need to take it every day throughout the year.
| Age | Doses | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| >75-year-old obese people (BMI >30 kg/m2) |
4000 to 8000 IU/day | Throughout the year |
| >75 years of age | 2000 to 4000 IU/day | |
| 65- up to 75-year-old obese people (BMI >30 kg/m2) | 1600 to 4000 IU/day | |
| 65 up to 75 years of age | 800 to 2000 IU/day | |
| 19 up to 65-year-old obese people (BMI >30 kg/m2) | 1600 to 4000 IU/day | |
| 19 up to 65 years of age | 800 to 2000 IU/day | Throughout the year when effective vitamin D3 synthesis is not ensured during the summer. |
| STANDARD VALUES FOR VITAMIN D3 SUPPLY TO THE BODY | |
|---|---|
| Severe deficiency | 0 up to 10 ng/ml |
| Significant deficiency | More than 10 up to 20 ng/ml |
| Suboptimal levels | More than 20 up to 30 ng/ml |
| Optimal levels | More than 30 up to 50 ng/ml |
| High levels | More than 50 ng/ml |

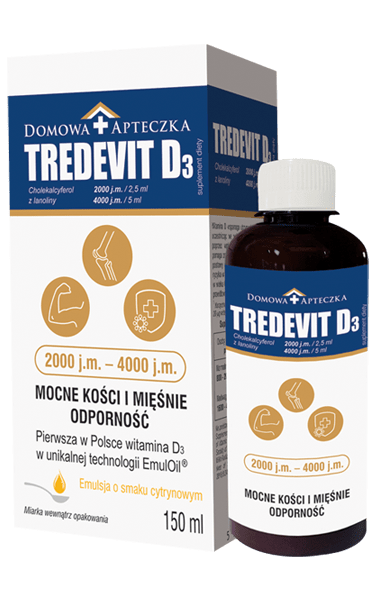
ABOUT THE PRODUCT


TREDEVIT D3 contains natural, lanolin-derived vitamin D3 which helps maintain strong bones and teeth due to its contribution to absorption of calcium and phosphorus. As vitamin D3 has an impact on normal muscle function, it helps reduce the risk of fall associated with postural instability and muscle weakness. Falls constitute a risk factor for bone fractures in both men and women aged 60 years or older. Moreover, vitamin D3 supports normal function of the immune system.
Regular and properly dosed vitamin D3 supplementation in elderly people contributes to:
- Stronger skeletal muscles
- Improved movement coordination and function of the lower limbs
- Less significant gait disorders or excessive swinging of the body

Recommended Tredevit D3 daily intake:
Adults up to 75 years of age – half a teaspoon (2.5 mL)
Adults over 75 years of age – 1 teaspoon (5 mL)
Tredevit D3 ingredients concerning the recommended daily intake of 2.5/5 mL:
Vitamin D3 2000 IU – 50 µg – 1000% DRV*
Vitamin D3 4000 IU – 100 µg – 2000% DRV
*Dietary Reference Value


BENEFITS OF TREDEVIT D3


A vitamin D3 supplement specially developed by the Team of Experts in the fields of pharmaceutical science, medicine and dietetics for people over 65 years of age.

The first vitamin D3 supplement in Poland based on the unique EmulOil® technology which ensures high levels of absorption and bioavailability.

Easy to swallow, lemon flavoured emulsion.

To be used with or without meals.

Vitamin D3 dosing consistent with the Recommendations for Poland.

It contains natural, lanolin-derived vitamin D3.

Sugar-free.

Gluten-free.

EmulOil® is an innovative form of emulsion which is easily absorbed by the body in a rapid process of digestion. The emulsified active ingredients are highly bioavailable.

VITAMIN D3 IN PEOPLE OVER 65 YEARS OF AGE

Following 65 years of age, the ability to produce vitamin D3 in the skin by the body on exposure to sunlight significantly decreases.
We should remember that ageing is a natural process and the specific body functions slow down or even disappear with age. This also pertains to the dermal synthesis of vitamin D3. The reason is a declining amount of 7-dehydrocalciferol (a substance necessary to synthesise vitamin D in the body) in the skin. Its amounts may even decrease by approximately 60% compared to young adults.
Following 65 years of age, deteriorating functions of the internal organs which are responsible for converting vitamin D in its active forms affecting the body are observed.
Renal functions which become gradually compromised with age may even block production of vitamin D active metabolites. Similar problems arise due to dysfunction of the liver where the first stage of vitamin D conversion into active 25-hydroxycholecalciferol occurs.
Following 65 years of age, absorption of vitamin D is hampered due to the digestive system ageing.
In the elderly, the ageing processes result in deterioration of the digestive system functions and compromised intestinal absorption of nutrients including vitamin D. Smaller amounts of gastric acid and digestive enzymes are secreted in the small intestine and bowel movement is weaker, which leads to digestive problems and poorer absorption of nutrients.2,4,6
1Chowdhury R. i wsp.: Vitamin D and risk of cause specific death: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort and randomised intervention studies. BMJ, 2014; 348:g1903 doi: 10.1136/bmj.g1903
2Granda D. i wsp.; Katedra Żywienia Człowieka; Wydział Nauk o Żywieniu Człowieka i Konsumpcji; Szkoła Główna Gospodarstwa Wiejskiego w Warszawie; Witamina D u osób starszych – funkcje, ryzyko niedoboru i wiedza seniorów; Kosmos Vol. 68, 2, 283 – 292, 2019
3Gruber B.M.; Fenomen witaminy D; Zakład Biochemii i Biofarmaceutyków, Narodowy Instytut Leków w Warszawie; Postepy Hig Med Dosw (online), 2015; tom 69: 127-139
4Kupisz-Urbańska M., Galus K.; Klinika Geriatrii, Warszawski Uniwersytet Medyczny; Epidemiologia niedoboru witaminy D u osób w podeszłym wieku — wybrane zagadnienia; Gerontologia Polska 2011, tom 19, nr 1
5Płudowski P. i wsp.; Zakład Biochemii, Radioimmunologii i Medycyny Doświadczalnej, Instytut „Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka”, Rekomendacje – Zasady suplementacji i leczenia witaminą D – Nowelizacja 2018 r.; Postępy Neonatologii 2018;24(1)
6Jurczak I., Barylski M., Irzmański R.; Pracownia Ergonomii i Fizjologii Wysiłku Fizycznego, Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi; Klinika Chorób Wewnętrznych i Rehabilitacji Kardiologicznej, Uniwersytet Medyczny w Łodzi; Znaczenie diety u osób w wieku podeszłym – ważny aspekt prewencji zdrowia czy nieistotna codzienność?; Geriatria 2011; 5: 127-133
7Tuchendler D., Bolanowski M.; Sezonowość zmian stężeń witaminy D w organizmie człowieka; Kliniczny Oddział Endokrynologii Szpitala Wojskowego we Wrocławiu; Katedra i Klinika Endokrynologii, Diabetologii i Leczenia Izotopami Akademii Medycznej we Wrocławiu; Endokrynologia, Otyłość i Zaburzenia Przemiany Materii 2010, tom 6, nr 1
8Wąsowski M., Czerwińska E., Marcinowska-Suchowierska E.; Otyłość – stan predysponujący do niedoborów witaminy D; Klinika Medycyny Rodzinnej, Chorób Wewnętrznych i Chorób Metabolicznych Kości, Centrum Medyczne Kształcenia Podyplomowego, Warszawa; Borgis – Postępy Nauk Medycznych 3/2012, s. 258-264
